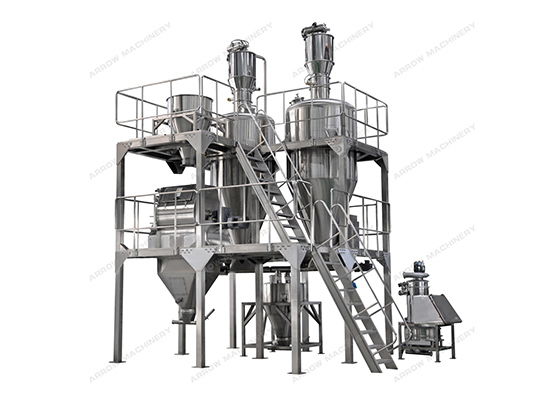
The processing of vegetable protein meat is divided into three steps: selection of protein raw materials, configuration and mixing, and maturation and extrusion. The original protein is separated from the protein of the selected beans; the protein is reshaped by using high-temperature water and pressure during the extrusion cooking process to form vegetable protein meat with a taste very close to animal meat.

Soy Protein
Advantages: low cost, common and easy to obtain; complete protein (contains 8 essential amino acids); drawing protein is more elastic, and gel emulsification is strong.
Disadvantages: Beany smell needs improvement; it is a potential allergen.
Soy protein is one of the most common plant meat raw materials. It is a complete protein and contains essential amino acids needed by the human body. Soy protein also has an advantage in simulating the chewy texture of meat. The soy silk protein made by extrusion method has a high degree of fiber structure and a higher degree of simulation. Soy silk protein is more elastic, tough and chewy, while wheat silk protein is finer and softer.
Pea protein
Advantage: Hypoallergenic, no phytoestrogens
Disadvantages: taste needs to be improved; the cost is higher than that of soybeans, and the production capacity is generally lower than that of soybeans; the texture protein has no silky feel; it is especially suitable for the processing of emulsified meat products and coarse ground meat products.
Pea protein is also a mainstream vegetable meat protein raw material. It is a hypoallergenic food. The branched-chain amino acids contained in it are important for relieving fatigue and muscle recovery.
Wheat Protein
Advantage: relatively low cost and easy to obtain
Disadvantage: wheat bran is a potential allergen
Wheat protein is also one of the commonly used protein materials, mainly composed of albumin, globulin, gliadin and glutenin, and wheat gluten mainly contains gliadin and glutenin [5]. The amount of 1% to 5% of wheat gluten is used as a binder in reorganized meat products, which can increase the viscoelasticity and hardness of the product, and improve the color stability, juice yield and water retention.
Peanut protein
Advantage: The texture of vegetable protein meat made of peanut protein is relatively softer, the surface is whiter, and the silk is softer
Peanut protein is a kind of vegetable protein with no protein heat denaturation and high nutritional value, which is refined by using high-quality domestic export-grade peanuts as raw materials, using low-temperature production of peanut protein and fragrant peanut oil industrial production technology.
It completely retains the nutrients in peanuts, has high soluble protein and NSI value, good water solubility, whiteness, light flavor, peanut-specific fragrance smell, nutritional value comparable to animal protein, rich in a large number of essential amino acids, Vitamins, trace elements and minerals have an effective utilization rate of 98%. They are easily digested and absorbed by the human body and contain fewer anti-nutritional factors than soybeans. It is a natural nutrient with low sugar, low fat, no cholesterol and high nutrition.
Mung Bean Protein
Advantages: hypoallergenic, no phytoestrogens, gelling and emulsifying properties
Disadvantage: Cost is higher than soybean
Chickpea Protein
Advantages: low allergens, high nutritional value, no phytoestrogens
Disadvantages: The cost is much higher than that of soybeans, and the production capacity is lower than that of soybeans. There are certain technical barriers to protein extraction.
fungal protein
Mycoprotein is also an applicable raw material. The British vegetarian brand Quorn is one of the representatives. They use the fungus Fusarium venenatum to make protein.
algae protein
Advantage: high protein content of algae, sustainable source of algae
Disadvantage: It can add natural flavor to plant seafood, but large-scale protein extraction technology is limited