We will introduce the characteristics of microwave equipment from the following aspects:
Microwave heating:
Microwave is an electric wave with a frequency of 300 MHz to 300 GHz. The water molecules in the heated medium material are polar molecules. Under the action of a rapidly changing high-frequency electromagnetic field, its polarity orientation will change with the change of the external electric field. This causes the movement of molecules to show the mutual friction effect. At this time, the field energy of the microwave field is transformed into heat energy in the medium, which increases the temperature of the material and produces a series of physical and chemical processes such as heating and puffing to achieve the purpose of microwave heating and drying.
Microwave sterilization:
Microwave sterilization is the result of using the combined effect of the thermal and biological effects of electromagnetic fields. The thermal effect of microwave on bacteria is to change the protein, so that the bacteria lose their nutrition, reproduction and survival conditions and die. The biological effect of microwave on bacteria is that the microwave electric field changes the potential distribution of the cell membrane, which affects the concentration of electrons and ions around the cell membrane, thereby changing the permeability of the cell membrane. Therefore, the bacteria are malnourished, unable to metabolize normally, cell structure and function disorder, and growth and development are inhibited. And death. In addition, the nucleic acid [RNA] and deoxyribonucleic acid [DNA], which can cause bacteria to grow normally and stably reproduce genetically, is caused by the relaxation, breakage and recombination of several hydrogen bonds, thereby inducing genetic mutations, or chromosomal aberrations or even breaks.
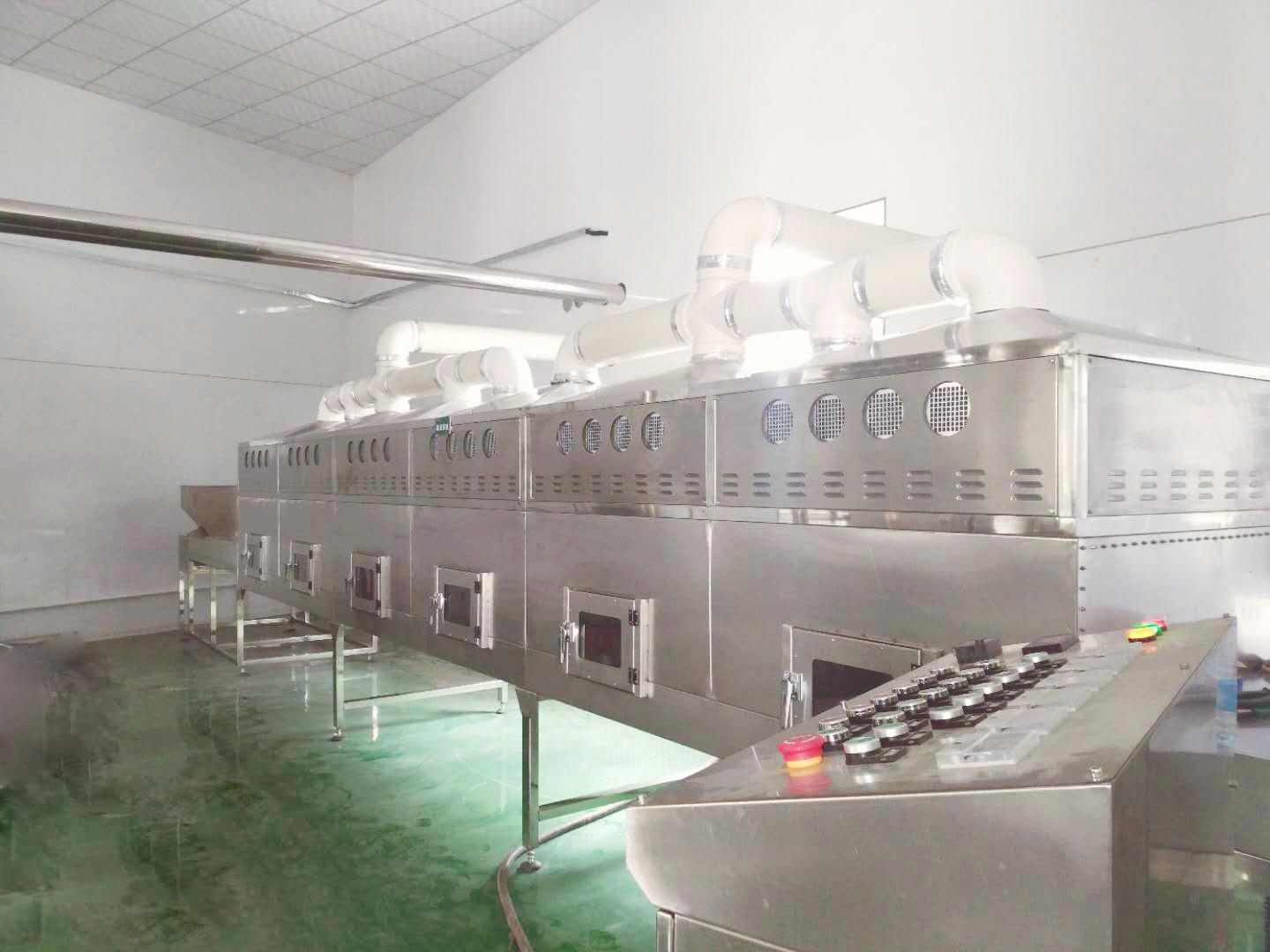

Microwave extraction:
A newly developed new technology that uses microwave energy to increase the extraction rate. Its principle is that in the microwave field, the difference in the ability to absorb microwaves makes certain areas of the matrix material or certain components in the extraction system be selectively heated, so that the extracted material is separated from the matrix or system and enters the medium. Among the extractants with small electric constant and relatively poor microwave absorption capacity; microwave extraction has the characteristics of simple equipment, wide application range, high extraction efficiency, good reproducibility, time saving, reagent saving, and low pollution. In addition to being mainly used for environmental sample pretreatment, it is also used in fields such as biochemistry, food, industrial analysis and natural product extraction. In China, there are relatively few research reports on microwave extraction technology used in Chinese herbal medicine extraction.
The mechanism of microwave extraction can be analyzed from the following three aspects: ①The microwave radiation process is the process of high-frequency electromagnetic waves penetrating the extraction medium to the microtubule bundle and adenocyte system inside the material. Due to the absorption of microwave energy, the temperature inside the cell will rise rapidly, so that the pressure inside the cell exceeds the ability of the cell wall to withstand expansion. As a result, the cell ruptures and the active ingredients inside it freely flow out and dissolve at a lower temperature. In the extraction medium. Through further filtration and separation, the desired extract can be obtained. ②The electromagnetic field generated by the microwave can accelerate the diffusion rate of the molecules of the extracted component from the solid interior to the solid-liquid interface. For example, when water is used as a solvent, under the action of a microwave field, water molecules change from a high-speed rotating state to an excited state, which is a high-energy unstable state. At this time, the water molecules either vaporize to strengthen the driving force of the extracted components, or release their own excess energy back to the ground state, and the released energy will be transferred to the molecules of other substances to accelerate their thermal movement, thereby shortening the extracted components The time for the molecules to diffuse from the inside of the solid to the solid-liquid interface, as a result, the extraction rate is increased several times, and the extraction temperature can be reduced to maximize the quality of the extract. ③Because the frequency of microwave is related to the frequency of molecular rotation, microwave energy is a kind of non-ionizing radiation energy that causes molecular motion due to ion migration and dipole rotation. When it acts on molecules, it can promote molecular rotation. If the molecule has a certain polarity, it can produce instantaneous polarization under the action of the microwave field, and make the polarity change movement at a speed of 2.45 billion times/s, which will produce bond vibration, tearing and inter-particle interaction. Friction and collision, and quickly generate a large amount of heat energy, which promotes the rupture of the cells, causing the cell fluid to overflow and diffuse into the solvent. In microwave extraction, the difference in the ability to absorb microwaves can make certain areas of the matrix material or certain components in the extraction system be selectively heated, so that the extracted material is separated from the matrix or system and enters the material with a smaller medium. In extraction solvents with relatively poor electrical constant and microwave absorption capacity.
Microwave thawing:
Microwave thawing is to heat up the whole frozen product, and the temperature rises from the freezing temperature (below -19~-22 C) to close to the freezing temperature (about 0~-4 C). The microwave thawing equipment has the characteristics of the overall temperature recovery of the frozen material, the small temperature gradient of the temperature recovery, that is, the temperature uniformity is good and the time required is short, and the temperature rise rate is easy to control. These characteristics make the frozen product thawing reach a more ideal state.
1. Frozen products can be heated as a whole to reduce the temperature unevenness between the thawing layers of the frozen products, and there is no recrystallization phenomenon of the frozen products when thawing as in the conventional method;
2. The time required for the thawing process is short, and bacteria and other microorganisms are not easy to multiply and grow.
3. Microwave heating has no thermal inertia. The temperature rise rate of the frozen material is controlled by the microwave output power, or the microwave energy supply rate, and is mutually synchronized.
4. The final temperature of microwave thawing is generally -2─-4 C. At this time, the frozen product has no dripping water, and it can also be cut with a knife.