Vegetable protein meat is a mechanical process of continuous heating of food ingredients through extrusion technology, followed by mixing, hydration, shearing, homogenization, compression, degassing, temperature and pressure accumulation, pasteurization, A series of operations such as flow alignment, forming, expansion and partial drying of food materials. During the extrusion process, vegetable protein is denatured by high temperature, high pressure, high shear, etc., so that the hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds, ionic bonds that maintain the protein structure are destroyed, and a plasticized melt is formed. Agglomeration, aggregation, and cross-linking form fibrous structures.
The production and preparation of vegetable protein meat technology includes low-moisture extrusion technology and high-moisture extrusion technology. The preparation of vegetable protein meat by screw extrusion technology has the advantages of simple operation and low product cost, and is suitable for simple food puffing and filling of meat products; the preparation of vegetable protein meat by low-moisture extrusion technology has mature process conditions and strong product flexibility, etc. However, follow-up processes such as rehydration are required, which is time-consuming; high-moisture extrusion technology has the advantages of high process integration and product texture closer to real meat, but the taste and flavor need to be further adjusted.
Plant protein meat is now divided into dry protein and wet protein. They are produced in different processes and have basically similar application fields.
(1) Dry protein:
After the high shear force, the extruder directly expands and needs about 10% dry moisture. Before the next step, it needs to replenish water by 2-3.5 times the water absorption rate.
Shape: pellets, flakes, balls, bars, chicken nuggets
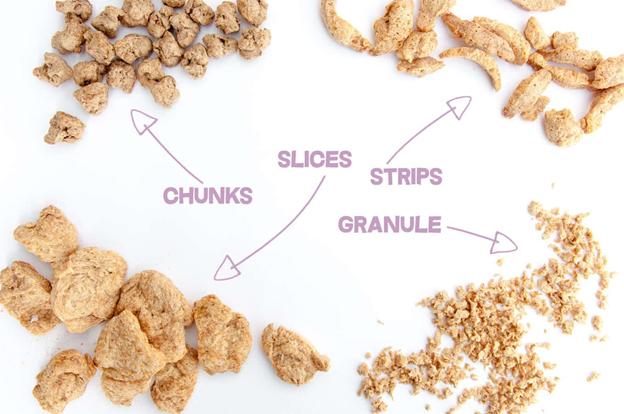
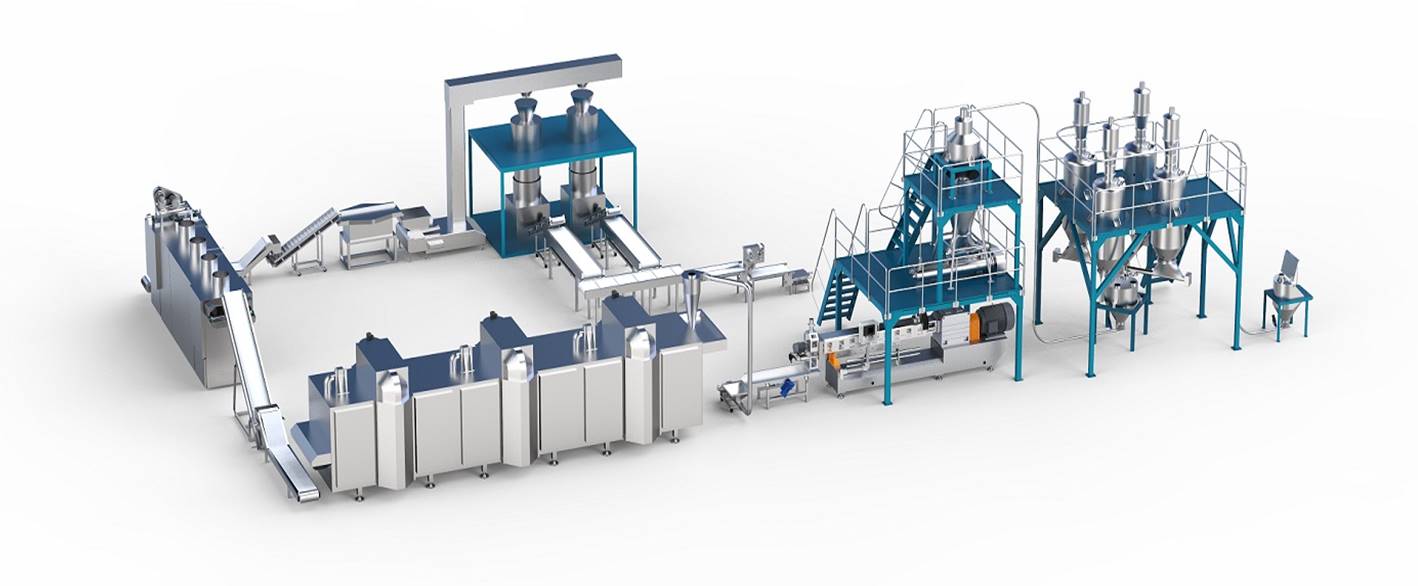
The production process is: batching—mixing—modulation—extrusion—forming—crushing—screening—drying—cooling—packaging
The subsequent processing process is: billet – rehydration – brine cooking – dehydration – forming

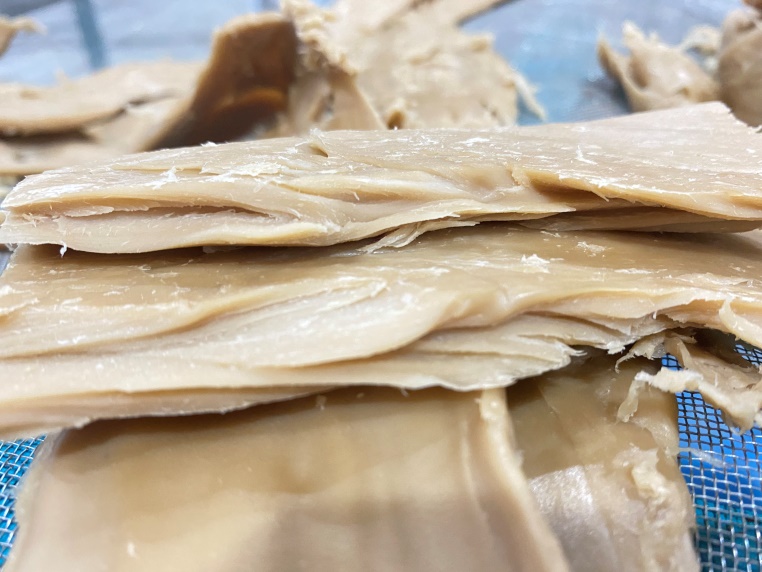
Some products require a silk-disconnecting process, in which the drawn protein is disassembled into filaments, and then reconstituted and shaped to give the finished meat a silky feel.



(2) Wet protein:
The filamentous fiber structure is more obvious. No drying is required. It needs to be refrigerated and frozen or the ideal raw material for the next processing of 50-70% high moisture content vegetable meat, and fully carry out the meat simulation process.
Raw materials: soybean, pea, sunflower, wheat, rice protein, etc.

The production process is: batching—mixing—extrusion—cutting—application
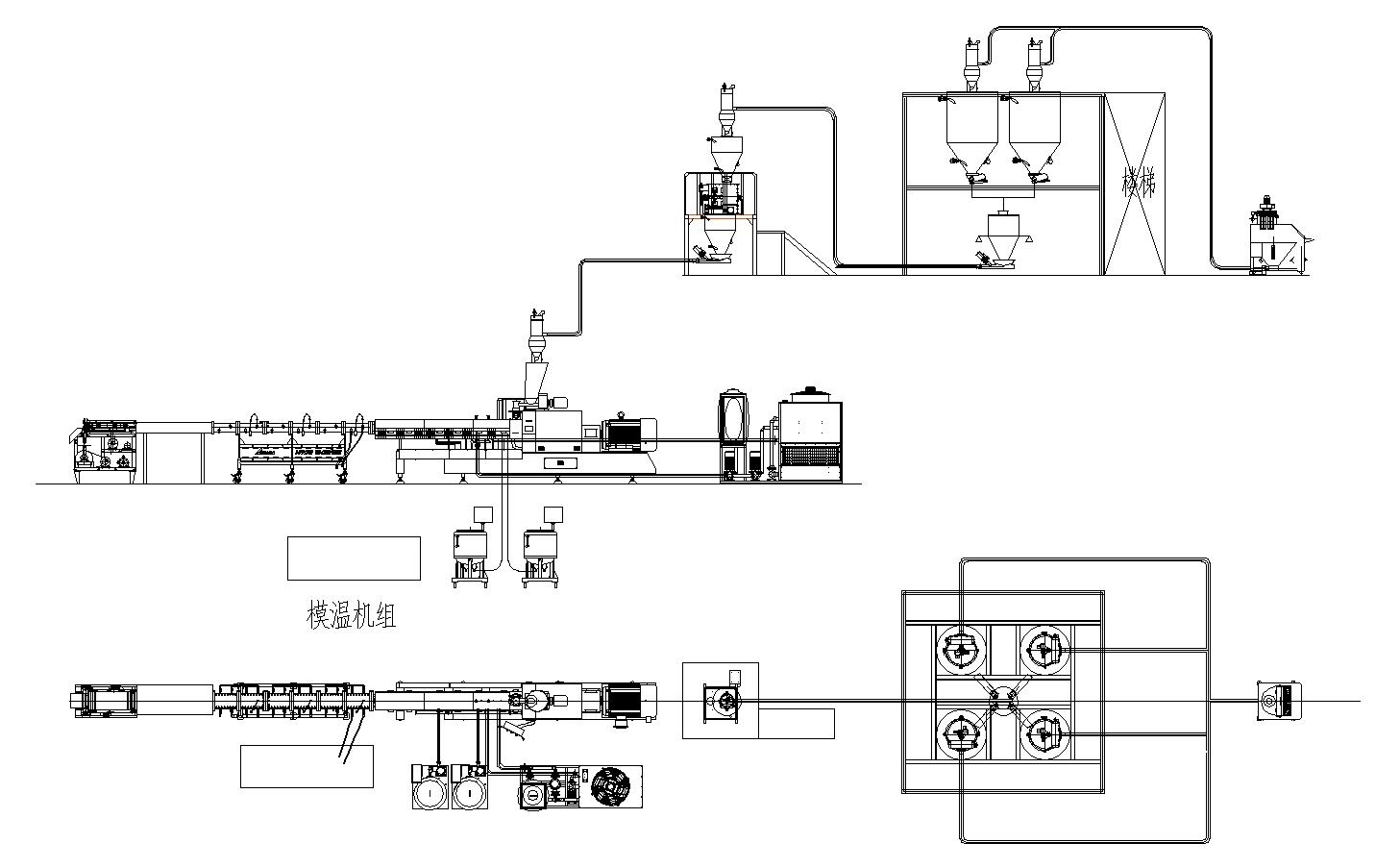
The follow-up processing technology is simpler than the dry method protein, and there is no need for rehydration.